Reading Time: < 1 minutes
-
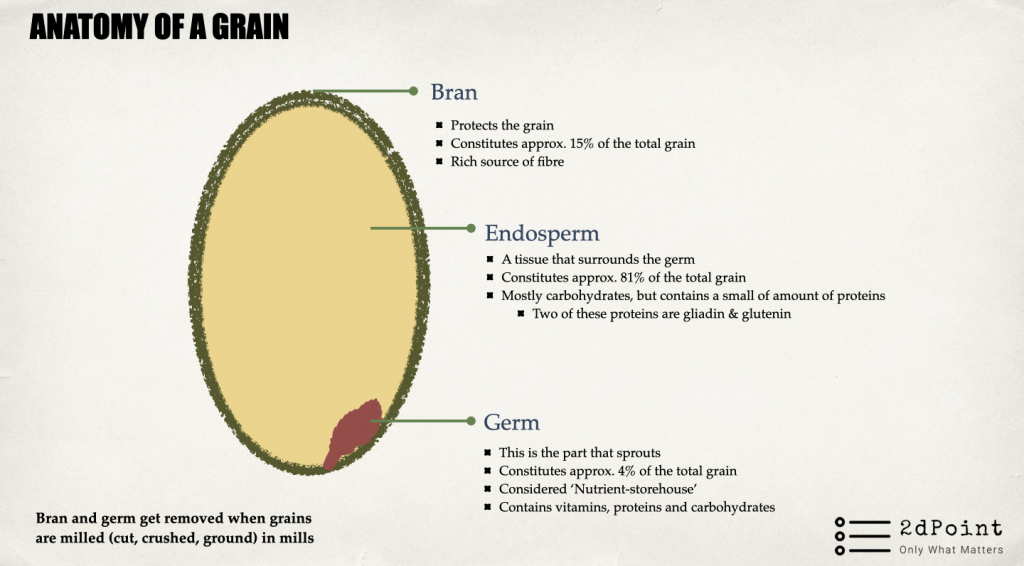
- Wheat grain has three parts: bran (outer shell) constitutes around 15%, the germ (a small part that sprouts) 4%, and endosperm (material that surrounds the germ) 81%.
- All three parts contain macronutrients (protein, carbohydrates, and fat) and different micronutrients (vitamin B, vitamin E, iron, etc.) in different quantities.
- E.g., bran has carbohydrates, iron, and vitamin B; germ has carbohydrates, vitamin E & protein, and endosperm has carbohydrates and a small amount of protein.
- The protein found in the endosperm is a mixture of hundreds of small proteins, and two out of these 100s are gliadin and glutenin.
- It is only when flour (which is mostly endosperm) is mixed with water that gliadin and glutenin bond together to form gluten.
- Without water and mixing, there would be no gluten, and it is because of the formation of gluten that the bread is elastic (stretchy).
- For some people, gluten causes problems – mostly two kinds: celiac disease and non-celiac gluten sensitivity (NCGS).
- In celiac disease, gluten can cause inflammation and damage the lining of the small intestine, making it hard for the body to absorb ingredients.
- This can cause belly pain, skin rashes, diarrhoea, bones diseases, fatigue, depression, and, in some cases, cancer.
- Blood tests are conducted to test the likelihood of someone having celiac disease, and if signs are present, a biopsy is done to confirm.
- Some people don’t have celiac disease, but they still feel symptoms when they eat gluten – this condition is called NCGS.
- People who don’t have celiac disease or NCGS have no reason not to consume gluten as it is a good source of protein, iron, and vitamin B.
- Other than wheat, barley and rye are also known to contain gluten.
- Gluten-free products are made using corn, rice, tapioca & potato starch; gums, baking powder, baking soda, egg, etc., are used to bring elasticity.
Reference shelf :