Reading Time: 2 minutes
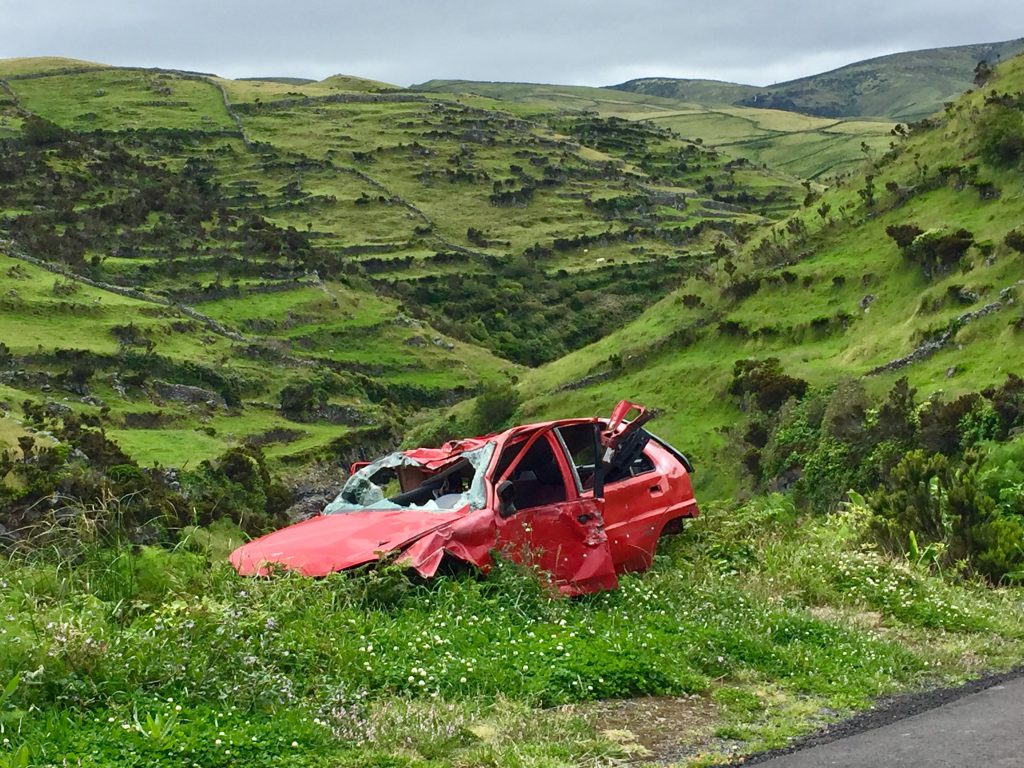
Globally, over 1 million road traffic deaths occur each year.
- The world has an average road death rate of 17.4 per 100,000 people and Sweden has 2.8; there are various reasons for such good road safety.
- Reason 1: A dedicated focus by the government.
- Between 1950 and 1965, the road deaths doubled in Sweden, mostly because Sweden had left-hand drive cars and they were driven on the left side of the road; this positioned the driver away from the centre of the road, and overtaking became dangerous.
- On 3rd September 1967, the government decided to switch from left-side-of-the-road driving to right-side-of-the-road driving.
- The traffic infrastructure was revamped and 360,000 road signs were changed in one day.
- Reason 2: Vision Zero. The number of road deaths has come down by 80% since 1970, while the number of cars and miles driven has doubled.
- Because of the success of the government initiatives in 1967, road safety began to be seen as one of the top priorities and Sweden built a Vision Zero >> to have ZERO car accidents by 2020.
- While the Vision Zero target couldn’t be achieved and the target date has been revised to 2050, the focus is very much there.
- Reason 3: It is very difficult to become a driver in Sweden.
- The road tests are far rigorous than many other developed countries and it can cost more than US$1,800 to learn to drive in Sweden.
- Reason 4: 2+1 Lane Roads.
- Roads with bad safety record (around 1500 kms) now have 2+1 lane roads.
- 2+1 road is a specific category of three-lane road, consisting of two lanes in one direction and one lane in the other, alternating every few kilometres, and separated with a steel cable barrier; therefore, sides take turn for overtaking.
- So, Traffic going from A to B will have two lanes for 10 kms and traffic from B to A will have one lane; after 10 kms A to B traffic will have one lane and traffic B to A will have two.
- Reason 5: Other initiatives such as strict policing (less than 0.25% drivers test positive in alcohol test), low urban zone speed limits, pedestrian zones, barriers between cars and cyclists etc.
Image courtesy of Photo by Dominika Kwiatkowska from Pexels
Reference shelf :